Duodenal Atresia Disease
Duodenal Atresia Disease - Diagnosis, Treatment & Care
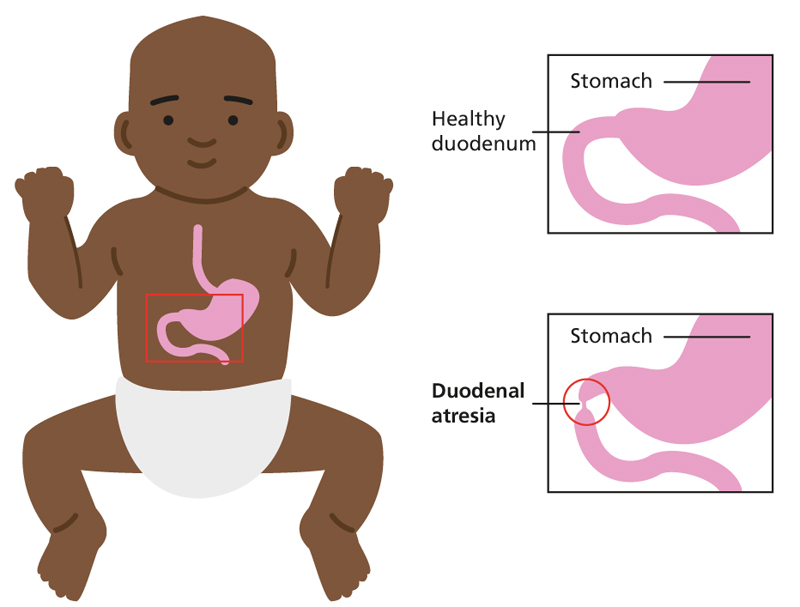
Duodenal Atresia is a congenital (birth) condition where a part of the duodenum — the first segment of the small intestine — is closed or blocked. This prevents the normal passage of food from the stomach to the intestines. Early diagnosis and timely surgical treatment can ensure a healthy future for the newborn.
Causes
Duodenal Atresia occurs due to improper development of the duodenum during fetal growth. It is often associated with:
- Down Syndrome (Trisomy 21)
- Premature birth
- Other congenital anomalies
Symptoms
Parents or doctors may notice signs soon after birth, including:
- Excessive vomiting (sometimes bile-stained)
- Inability to tolerate feeding
- Swollen upper abdomen
- Dehydration or poor weight gain
Diagnosis
This condition can be detected:
- Before birth through prenatal ultrasound showing “double bubble” sign
- After birth using X-rays, abdominal ultrasound, and physical examination
Treatment
The only effective treatment for Duodenal Atresia is corrective surgery. A pediatric surgeon creates a new connection between the stomach and intestine to bypass the blocked segment. Post-surgery:
- Feeding is started gradually
- Baby is monitored in NICU
- Full recovery is expected with proper care
Why Early Treatment Matters
Timely medical intervention ensures:
- Normal digestion
- Healthy growth and development
- Prevention of complications like dehydration or infection
When to See a Specialist
If a newborn shows feeding difficulty, persistent vomiting, or abdominal swelling, consult a Pediatric Surgeon / Neonatal Specialist immediately.
