Atresia Disease
What is Atresia?
Atresia is a congenital (present at birth) condition where a normal opening or passage in the body is absent or abnormally closed. This can affect various organs, such as the intestines, bile ducts, esophagus, or nasal passages, leading to obstruction or improper organ function. Early diagnosis and timely treatment are essential to prevent complications and ensure healthy development.
Types of Atresia
Atresia can occur in different parts of the body, including:
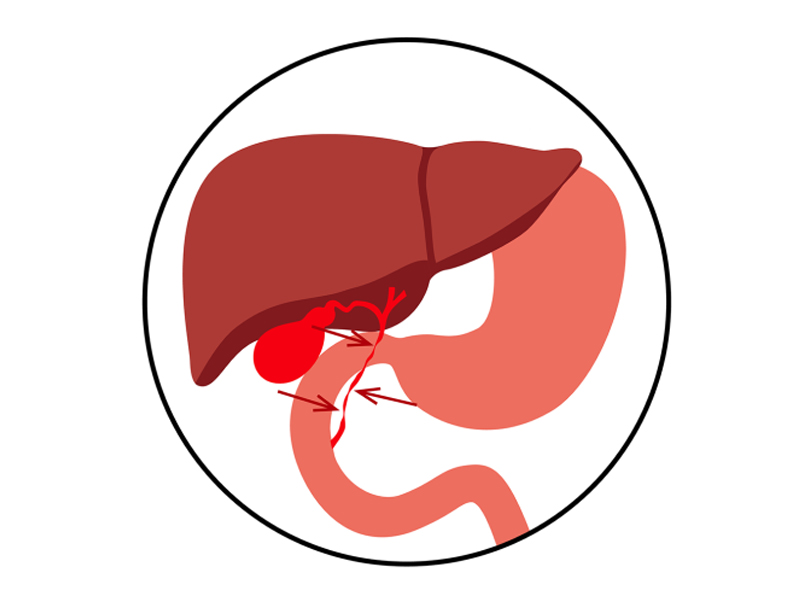
- Biliary Atresia: Blockage or absence of bile ducts, causing liver and bile flow problems.
- Esophageal Atresia: The esophagus (food pipe) ends in a blind pouch and does not connect to the stomach.
- Intestinal Atresia: Obstruction in the small or large intestine, preventing food movement.
- Choanal Atresia: Blockage in the nasal passages, making breathing difficult for newborns.
- Pulmonary Atresia: A heart defect where the pulmonary valve does not form properly, affecting blood flow to the lungs.
Common Symptoms
Symptoms depend on the type of atresia but may include:
- Difficulty feeding or swallowing
- Vomiting or bloating in newborns
- Yellowing of skin (jaundice)
- Breathing difficulties
- Poor weight gain
- Abdominal swelling
Diagnosis
Atresia is often diagnosed through:
- Prenatal Ultrasound (before birth)
- X-rays and Imaging Tests (after birth)
- Blood Tests
- Endoscopy or Echocardiogram, depending on the organ affected
Treatment Options
Most types of atresia require surgical correction to restore normal function. Treatment may include:
- Reconstructive Surgery: To connect or open the blocked passages.
- Liver or Bowel Surgery: For biliary or intestinal atresia.
- Post-surgical Care & Nutritional Support: To promote recovery and growth.
Why Choose Us?
- Expert pediatric and neonatal surgical care
- Advanced diagnostic facilities
- Comprehensive post-operative care
- A compassionate team dedicated to your child’s well-being
